Which Organs Receive Postganglionic Axons From the Superior Mesenteric Ganglion
Distal parts of the ureters and most of the reproductive organs. These responses are important during Fight-or-flight response of the ANS.
The Autonomic Nervous System Neupsy Key
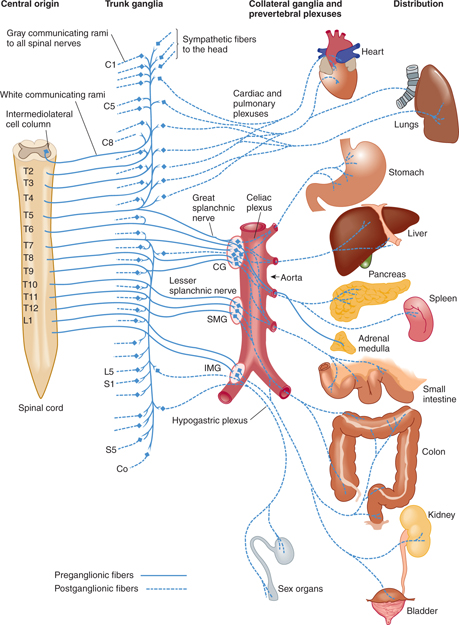
The colon large intestine is innervated by neurons from the superior mesenteric ganglion while in the rectum they originate in the inferior mesenteric ganglion.

. This pelvic plexus also contains parasympathetic nerves. Which organs receive postganglionic axons from the superior mesenteric ganglion. Increased secretion from gastric glands.
The least splanchnic nerve T12 sends fibers either to the superior mesenteric ganglion or the inferior mesenteric ganglion. Parasympathetic fibers distribute to the stomach and proximal duodenum from the celiac branches of the vagus nerve. Conscious the autonomic and somatic nervous system can be.
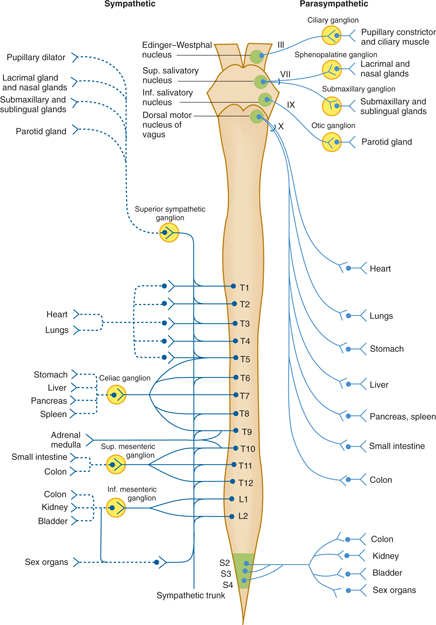
The parasympathetic division is also known as the craniosacral division of the autonomic systemThis is because its preganglionic fibers originate in the brain specifically in the midbrain medulla oblongata and pons and in the second through fourth sacral levels of the spinal columnThese pre-ganglionic parasympathetic fibers synapse in ganglia that are located. The large intestine and kidney are the target organs from this ganglion in addition to a contribution to the pelvic plexus. Centrally mediated pathways account for longer reflexes.
Similarly what organs receive fibers from superior mesenteric ganglion. Crowcroft et al 1971. The celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia receive their preganglionic input from the greater and lesser thoracic.
Subsequently question is what organs receive fibers from superior mesenteric ganglion. Which autonomic ganglion provides postganglionic axons to the lacrimal glands and small glands of the nasal cavity oral cavity and palate. The postganglionic axons of the Superior cervical ganglion innervate the eye and lacrimal gland and cause vasoconstriction of the iris and sclera pupillary dilation widening of the palpebral fissure and the reduced production of tears.
The celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia receive their preganglionic input from the greater and lesser thoracic splanchnic. Which organs receive postganglionic axons from the superior mesenteric ganglion. Dilation of the pupils allows for an increased clarity in vision and.
This pelvic plexus also contains parasympathetic nerves. The large intestine and kidney are the target organs from this ganglion in addition to a contribution to the pelvic plexus. In the stomach and intestines the sympathetic output from celiac ganglion causes sphincter contraction and decreased motility.
Sympathetic division which division of the autonomic nervous system is also known as the thoracolumbar division. 60 rows What organs receive postganglionic axons from the superior mesenteric ganglion. Sympathetic nerves arising from the inferior mesenteric ganglion supply the descending and sigmoid colon and rectum.
The stomach and proximal duodenum receive abundant sympathetic innervation from the celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia and to a lesser extent from the thoracic sympathetic trunk ganglia. Postganglionic fibers join the superior mesenteric plexus and travel to the midgut organs third part of the duodenum through the first two thirds of the transverse colon. Kidneys Proximal ureters Rectum Stomach Jejunum of small intestine Liver Kidneys.
Kidneys proximal ureters jejunum of small intestine Which cranial nerve supplies parasympathetic innervation to the thoracic organs most abdominal organs and the gonads. These neurons contain axons that innervate the lower esophageal sphincter the stomach the upper small intestine liver and pancreas. The celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia receive their preganglionic input from the greater and lesser thoracic splanchnic nerves.
Stomach spleen liver gallbladder duodenum pancreas Which organs are innervated by posganglionic axons from the celiac ganglion. Postganglionic sympathetic axons from the thoracic sympathetic trunk ganglia and preganglionic axons from the vagus nerve come together to form the. Facial nerve CN VII the greater petrosal nerve is a branch of the parasympathetic preganglionic axons of the.
Postganglionic fibers radiate from the celiac ganglia along the course of the blood vessels and innervate the abdominal viscera which are derived from the embryonic foregut 25 ie much of the distal esophagus stomach duodenum small intestine ascending and proximal transverse colon. The sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system is anatomically known as the _____ division. These three ganglia are known collectively as the prevertebral ganglia.
Rectum Reproductive organs Urinary bladder Match the cholinergic receptor with. Secondly what organs receive fibers from superior mesenteric ganglion. The small intestine is innervated by postganglionic axons dashed orange line originating in the celiac ganglion.
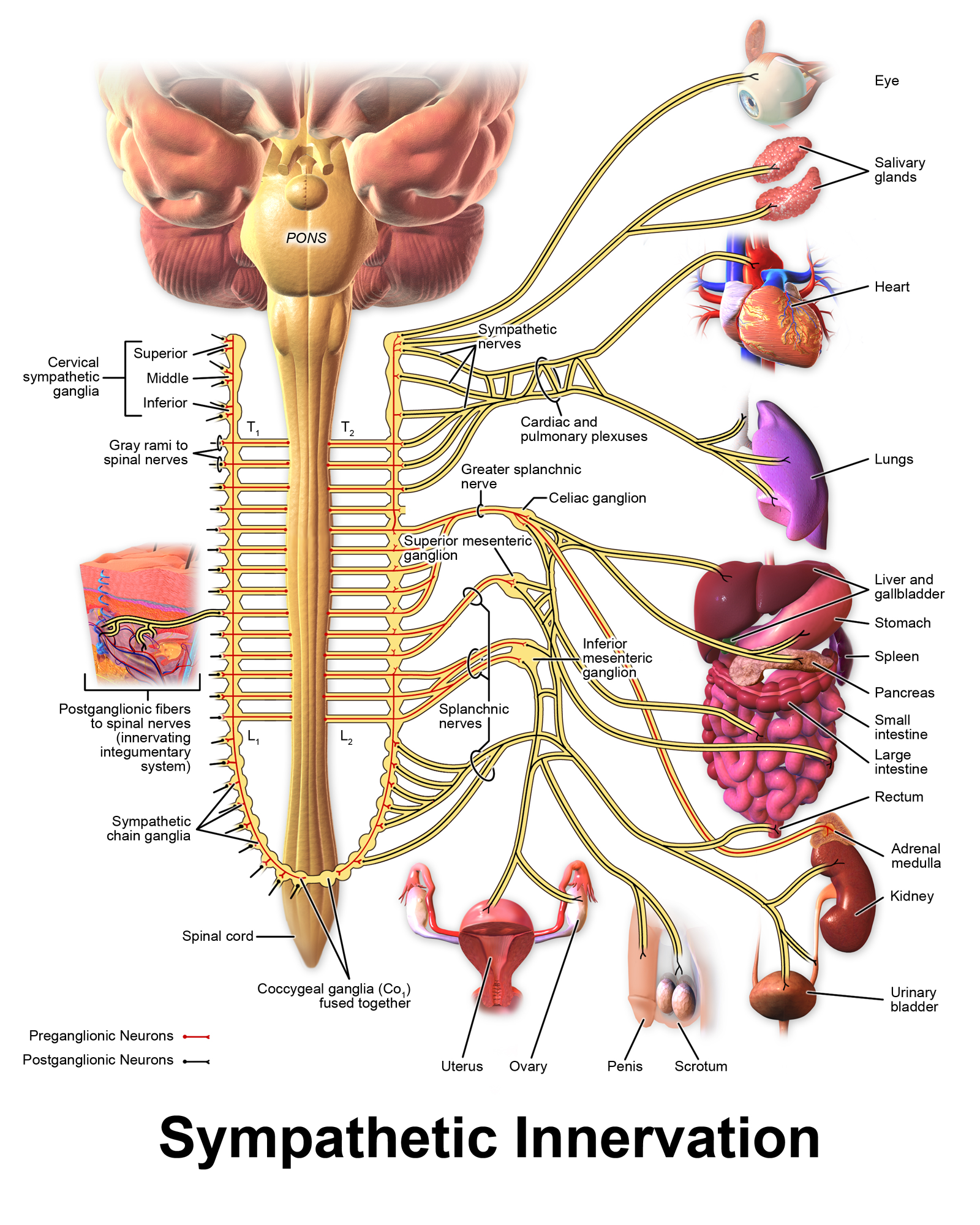
Furthermore which structure is supplied by postganglionic fibers originating in the superior mesenteric ganglion. Large intestine rectum urinary bladder distal parts of the ureters and most of he reproductive organs which organs receive postganglionic axons from the inferior mesenteric ganglion. Because they connect to all spinal nerves cervical thoracic lumbar sacral coccygeal.
Which organs receive postganglionic axons from the superior mesenteric ganglion. The celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia receive their preganglionic input from the greater and lesser thoracic splanchnic nerves. And the inferior mesenteric ganglion innervates the descending colon sigmoid colon rectum urinary bladder and sexual organs.
Which organs receive postganglionic axons from the superior mesenteric ganglion. The large intestine receives parasympathetic nerves from the pelvic nerve arising from spinal. The intestine receives neuronal input from prevertebral ganglia the celiacsuperior mesenteric ganglion complex solar plexus the inferior mesenteric ganglion and the pelvic plexus and nerve cell bodies in the gastrointestinal wall project to these prevertebral ganglia forming a reflex loop see Kuntz and Saccomanno 1944.
The proximal large intestine is supplied by sympathetic nerves arising from the superior mesenteric ganglion. Which organs are innervated by postganglionic axons from. Vigorous contraction of rectal smooth muscle.
Which organs receive postganglionic axons from the inferior mesenteric ganglion. This varies from source to source so we won. What organs receive fibers from celiac ganglion.

Innervation Of Cardiac Skeletal And Smooth Muscle The Table Left Download Scientific Diagram

Inferior Mesenteric Plexus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Osteopathic Management Of Gi Disorders Flashcards Quizlet

The Autonomic Nervous System Medical Mnemonics Autonomic Nervous System Medicine Studies

Inferior Mesenteric Plexus An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

149 Autonomic Ganglia Of Head Neck And Pupillary Light Reflex Flashcards Quizlet

Fig Glossopharyngeal Nerve Transmits Signals Ppt Download

Schematic Showing The Origin And Distribution Of The Ovarian Plexus Download Scientific Diagram
The Autonomic Nervous System Neupsy Key

Autonomics Of The Abdomen Sciencedirect

Overview Of Sympathetic Pathways Preganglionic Axons Of The Sympathetic Division Extend From The T1 L2 Spinal Cord Anatomy Spinal Nerve Cranial Nerves Anatomy

The Autonomic Nervous System The Nervous System Medical Physiology 2e Updated Edition With Student Consult Online Access 2e Medical Physiology Boron 2nd Ed

Gi Nerves Of The Abdomen Ach 1 Hr Flashcards Quizlet

Prevertebral Ganglia And Plexus Anatomy Mitch Medical Healthcare

Anatomy Autonomic Nerves Of The Abdominal Cavity Rectum And Anal Canal Flashcards Quizlet

Schematic Showing The Origin And Distribution Of The Ovarian Plexus Download Scientific Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment